[ad_1]
The current ransomware assaults on Colonial Pipeline and JBS led to a flurry of calls to ban Bitcoin (and cryptocurrency usually) as enabling and incentivizing these assaults.[1] Given the problem of monitoring the perpetrators, the argument goes, cryptocurrency is a uniquely interesting methodology of cost to hackers. Take away the hackers’ simple skill to receives a commission and also you cut back the motivation to hold out the assault. Bitcoin defenders level out that plenty of issues are utilized in prison exercise that we aren’t ready to ban. Cryptocurrency critics reply that, for all its promise, cryptocurrency stays devoid of a single constructive use case, and that its major makes use of are for speculative funding and prison exercise.[2] On Sunday, June 6, former President Trump remarked that Bitcoin was “a rip-off” that competed with the U.S. greenback.[3] Then on Monday, June 7, federal authorities introduced that they’d traced and seized thousands and thousands of {dollars} that Colonial Pipeline paid within the assault, the primary such publicized ransomware cost restoration.[4] What, if any, implications does that restoration have for the talk over banning cryptocurrency?
This explainer unpacks the current occasions, their which means, and suggests what could be coming subsequent by way of regulation enforcement and regulatory exercise for cryptocurrency.
What Occurs in a Ransomware Assault?
A hacker penetrates an organization’s pc system and encrypts the corporate’s knowledge, thereby bringing operations to a halt. The hacker then holds the info hostage till a ransom is paid. If the demand is made for cost in Bitcoin or one other cryptocurrency, the sufferer has to open an account on a cryptocurrency change, purchase Bitcoin, and ship it to the hacker’s digital pockets in change for the decryption key. The important thing permits the corporate to revive entry to its knowledge so its operations can resume. The hacker, in the meantime, strikes the cost via cryptocurrency exchanges and “mixers”—companies that mix cryptocurrency from varied sources to cover its origin, thereby laundering the ransom cost.[5]
Why is Cryptocurrency the Cost of Alternative for Ransomware Hackers?
Cryptocurrency is beneficial for ransomware funds as a result of its pseudonymous high quality; even when you see the ultimate vacation spot pockets into which the ransom cost is deposited, you’ll be able to’t see who owns or controls the pockets. This has allowed ransomware assaults to be carried out with relative impunity. This impunity, in flip, has led to an explosion of ransomware assaults and the prevalence of a ransomware firm DarkSide, which leases its ransomware to hackers in change for a portion of any ransom paid. DarkSide, the recipient of the Colonial Pipeline ransom cost, has collected greater than $90 million in ransom funds within the final 12 months, in line with Elliptic, a blockchain analytics agency.[6]
Ransomware assaults demanding cryptocurrency have gotten worse in each nature and quantity. In previous years, ransomware hackers stole knowledge and threatened to launch it or promote it on-line.[7] A horrible act to make certain, however not one which essentially paralyzes an organization. Extra just lately, nonetheless, hackers have more and more introduced operations to a halt by encrypting recordsdata essential for persevering with the enterprise. Assaults are, due to this fact, extra prone to be debilitating, giving the hackers extra leverage.
Hackers have used this leverage to strike more durable and extra incessantly. The variety of ransomware instances reported to the FBI went up by roughly 66% in 2020,[8] and the typical ransomware cost has quadrupled in lower than two years, going from $12,000 in This autumn 2019 to $54,000 in Q1 2021.[9] A report by blockchain analytics agency Chainalysis famous that though previous to Q1 2020, it by no means noticed a ransomware cost above $6 million, since then it has recognized at the least one per quarter. [10]
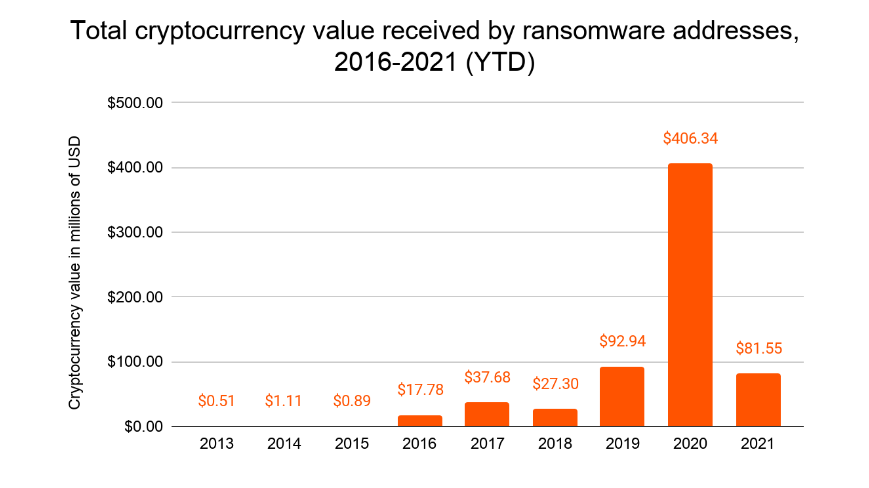
Supply: Chainalysis: Ransomware 2021: Critical Mid-Year Update [Report Preview].
When it comes to complete worth paid, Chainalysis discovered that cryptocurrency worth acquired by ransomware addresses went from simply over $37 million in 2019, to simply over $92 million in 2019, to greater than $406 million in 2020. And as of Might 10, 2021, greater than $81 million in cryptocurrency had been despatched to ransomware addresses.
So Why Not Ban Cryptocurrency?
However the considerations about cryptocurrency facilitating ransomware assaults, a ban is usually thought by these within the business and the federal authorities alike to be overbroad, logistically impractical, and prone to trigger aggressive hurt to the U.S.[11] Though assorted requires a ban have been revealed just lately,[12] federal regulators and regulation enforcement officers are optimistic that the regulation will catch as much as the chance.
As an example, Chairman of the SEC Gary Gensler, who beforehand taught a course at MIT on cryptocurrency and blockchain, has described himself as an “optimist” on the blockchain know-how used to file Bitcoin transactions, saying that he desires it to succeed whereas defending monetary stability, traders, and shoppers.[13] In April, SEC Commissioner Hester Peirce commented that “it could be a silly factor for the federal government to attempt to try this [ban Bitcoin],” {that a} “authorities might say it’s not allowed right here however folks would nonetheless have the ability to do it and it could be very laborious to cease folks from doing it [transacting in Bitcoin],” including that “we’d be lacking out on the innovation round bitcoin and different digital property if we determined to attempt to cease them.”[14] The identical month, Michael Morell, former Deputy Director of the CIA authored a paper arguing (amongst different issues) that the blockchain ledger on which Bitcoin transactions are recorded is a really efficient and under-utilized crime-fighting and intelligence gathering device.[15]
Morello cites present and former federal officers of the view that it “is less complicated for regulation enforcement to hint illicit exercise utilizing Bitcoin than it’s to hint cross-border criminality utilizing conventional banking transactions, and much simpler than money transactions,” and who examine the blockchain ledger recording Bitcoin transactions to “having the entire world be a witness to paying somebody $2,000 in a darkish alley.”[16] To be honest, having the entire world witness the cost is just not the identical as having it witness the identification of the payee. In any occasion, Morello’s confidence in regulation enforcement’s tracing skill was born out on June 7 when federal authorities introduced the restoration of thousands and thousands of {dollars} paid within the Colonial Pipeline ransomware assault.[17]
How Did the FBI Get better the Ransom Cost?
On this case, the FBI appeared to catch a fortunate break, as no monitoring via mixers or different obscuring channels was required. Inside days of the Might 8 ransom cost by Colonial Pipeline, the analytics agency Elliptic recognized the Bitcoin pockets that acquired the cost and noticed that it had acquired Bitcoin funds since March totaling $17.5 million.[18] Though many of the funds have been moved out on Might 9, simply over two million {dollars} remained in the identical account it was paid into till it was seized by the FBI via a court-approved seizure warrant.
On the similar time, the actions of figuring out the pockets and acquiring a seizure warrant, by themselves, wouldn’t give the FBI entry to the ransom funds. The FBI additionally wanted the non-public key to entry the pockets. The agent affidavit submitted in help of the seizure warrant utility states that the FBI was in possession of the non-public key, however doesn’t specify the way it was obtained. Nor has the FBI mentioned publicly the way it obtained the important thing. A couple of prospects famous within the press are that (1) the FBI was tipped off by somebody related to the assault, or related to DarkSide, (2) one of many hackers was careless in discussing the important thing over a communications channel and the FBI had already obtained a search warrant for (because the FBI had been investigating DarkSide for the final 12 months, or (3) from “leveraging data it obtained from Bitcoin or from the cryptocurrency change the place the cash had been bouncing from one account to a different because it was first paid.”[19] On condition that a few of the cash by no means left the unique account into which it was deposited, presumably which means that regulation enforcement gained perception from the opposite funds that have been transferring between accounts. For now, nonetheless, we’re left to invest as to how the important thing was obtained.
What Does the Restoration Imply for Banning or Regulating Bitcoin?
On condition that regulation enforcement has a capability to trace and recuperate ransomware funds in a method that even every week in the past appeared unlikely, the current restoration might each deter such assaults and quiet the calls to “ban cryptocurrency” usually. However recovering the cost is just not the identical as figuring out and prosecuting the hacker. Neither is it the identical as stopping such assaults within the first place.
De-anonymizing transactions would assist obtain each the prevention and prosecution goals, as regulators appear to agree. A would-be hacker whose identification is discoverable is extra seemingly deterred from making an attempt such an assault. When it comes to new requirements, the Monetary Motion Job Pressure (“FATF”), a bunch of 200 nations and jurisdictions that units AML and different requirements for digital property and digital asset service suppliers (“VASPs”), launched a draft of latest steering in March that appears to recommend prohibiting peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges and privateness cash (i.e., Anonymity-Enhanced Cryptocurrencies (“AECs”) that use further options to hide details about transactions).[20] Concern about privateness cash is just not restricted to FATF. Michael Morell commented that the most well-liked privateness coin—Monero—sees the next proportion of illicit exercise inside its total transaction quantity, that one recognized ransomware group (Sodinokibi) accepts funds solely in Monero and that some ransomware operators provide discounted charges to victims who paid in Monero or different AECs.[21] South Korea banned Monero and different privateness cash late final 12 months, and plenty of cryptocurrency exchanges select to not record Monero given the dangers related to it.[22]
We are able to additionally count on higher enforcement of current Know Your Buyer (KYC) and AML obligations and requirements. As an example, cryptocurrency exchanges, custodial pockets corporations, and crypto cost processors (amongst others) should register as cash companies companies with FinCEN, have AML applications that specify the KYC data collected, and appoint a compliance officer to watch transactions and file Suspicious Exercise Experiences (“SARs”) and Foreign money Transactions Experiences (“CTRs”) for transactions in extra of $10,000. These processes are vital not just for potential regulation enforcement monitoring within the occasion against the law happens, however clearly for crime prevention and for constructing shopper belief and confidence, a necessity for widespread adoption of cryptocurrency. New candidates have to know that criminals are being screened for and saved out.
Higher federal sources are additionally being dedicated to reinforce regulation enforcement sophistication in monitoring and prosecuting crypto crimes. [23] As talked about in a prior consumer advisory, the U.S. Division of Justice (“DOJ”) launched its Cryptocurrency Enforcement Framework in October 2020, and the IRS (amongst different businesses) has been contracting with blockchain analytics companies to work on tracing the “untraceable” privateness cash and different currencies, a challenge that appears to have been at the least partially profitable.[24] Only a week in the past, DOJ launched the Ransomware and Digital Extortion Job Pressure devoted to combating combatting ransomware assaults, which FBI Director Christopher Wray has in comparison with the nationwide safety risk the nation confronted after terrorist assaults of the September 11, 2001.[25] The brand new job power, a public-private partnership, consists of representatives from the FBI and the US Secret Service in addition to main tech and safety corporations,[26] and is predicted to advocate harder KYC laws and licensing necessities in addition to centralize efforts to fight and reply to ransomware assaults.
[View source.]
[ad_2]
Source link